

Password-based authentication for Git has been removed in favor of more secure authentication methods. Alternatively, you can use a credential helper like Git Credential Manager. When Git prompts you for your password, enter your personal access token. The next time you git fetch, git pull, or git push to the remote repository, you'll be asked for your GitHub username and password. Verify that the remote URL has changed.Change your remote's URL from SSH to HTTPS with the git remote set-url command.List your existing remotes in order to get the name of the remote you want to change.Change the current working directory to your local project.
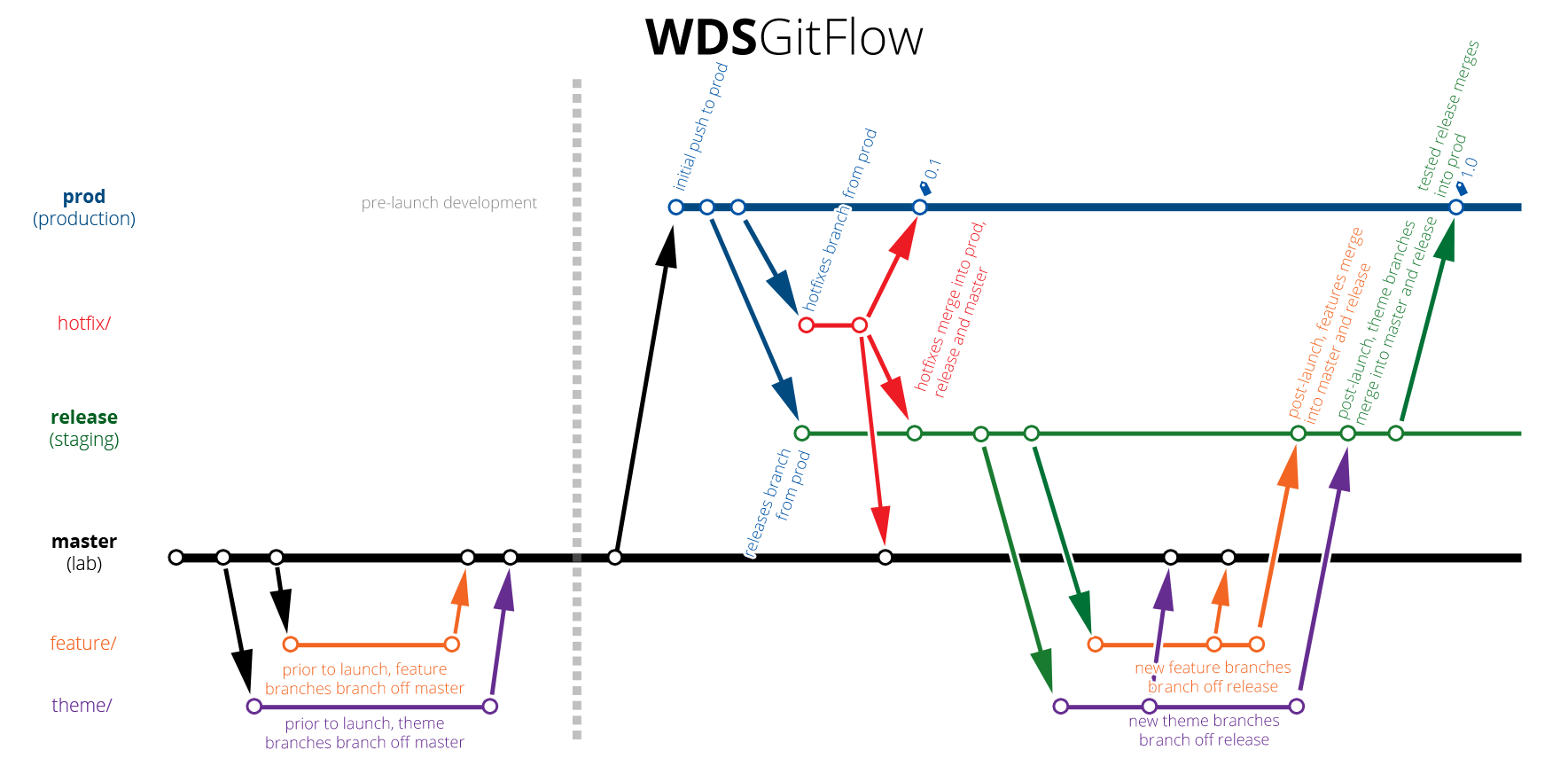
If you're updating to use SSH, your URL might look remote URLs from SSH to HTTPS.If you're updating to use HTTPS, your URL might look like:.For example, origin or upstream are two common choices. The git remote set-url command takes two arguments: Tip: For information on the difference between HTTPS and SSH URLs, see " About remote repositories." The git remote set-url command changes an existing remote repository URL. For more information, see " Removing a remote repository" below. Delete the existing remote repository before you add the new remote.For more information, see " Renaming a remote repository" below.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
